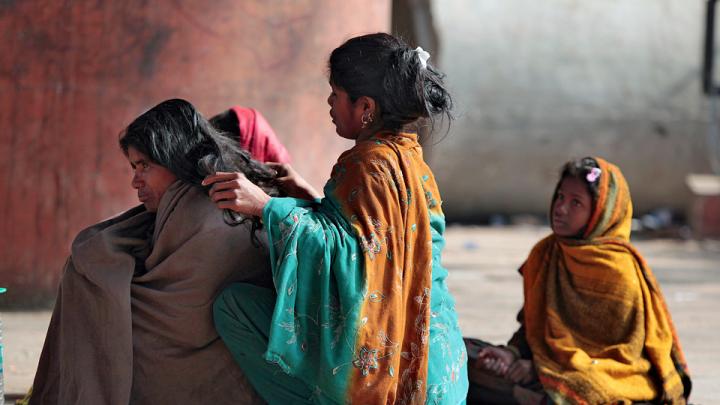
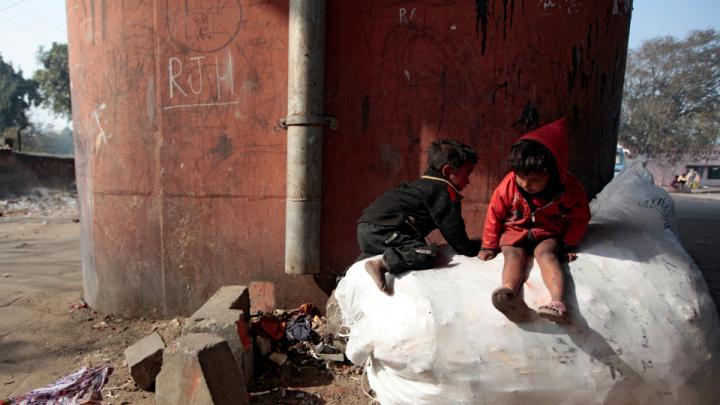
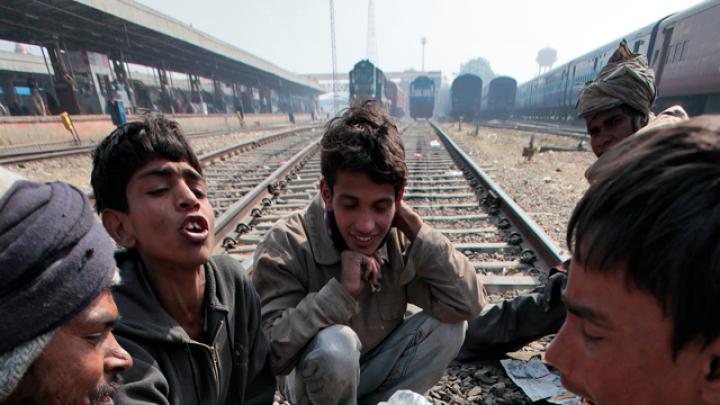
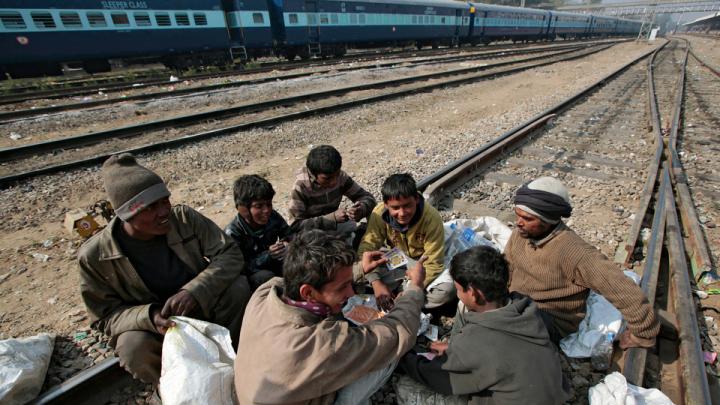
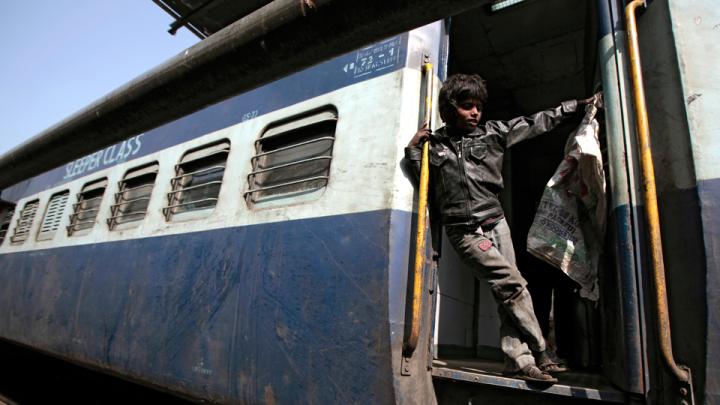
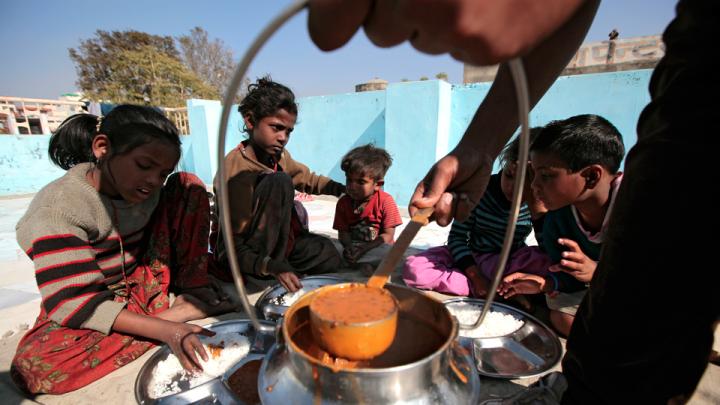
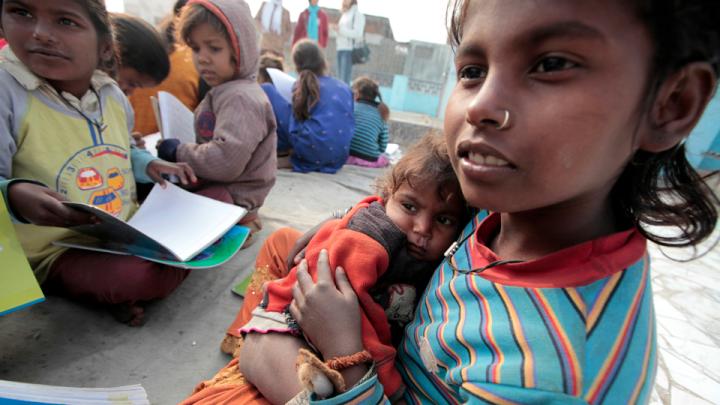
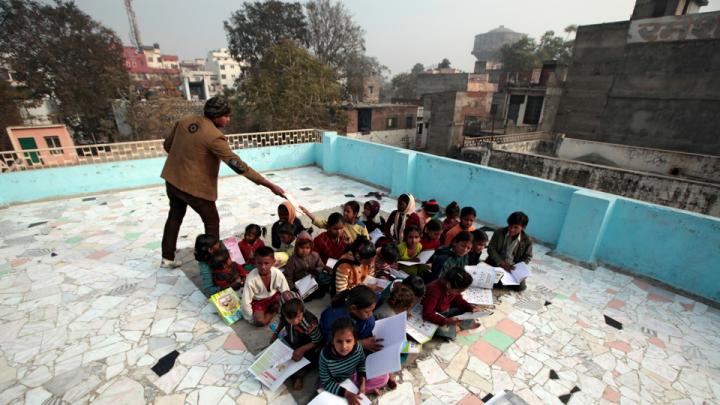
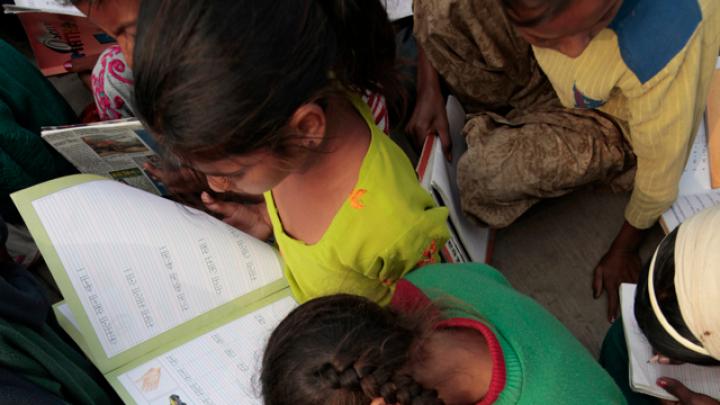
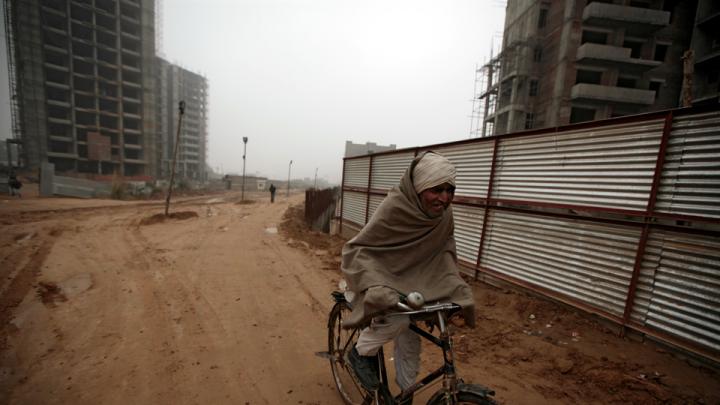
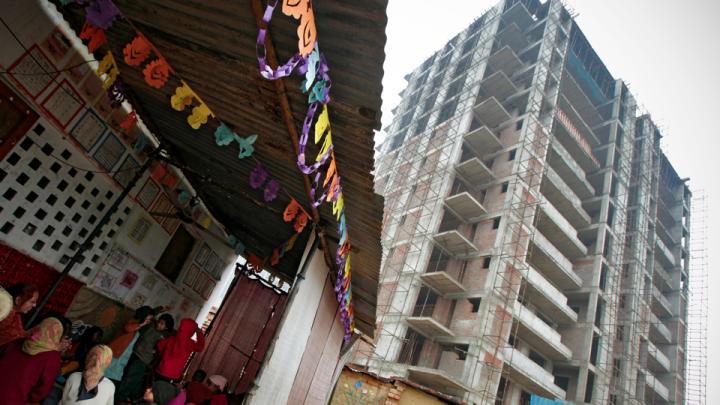
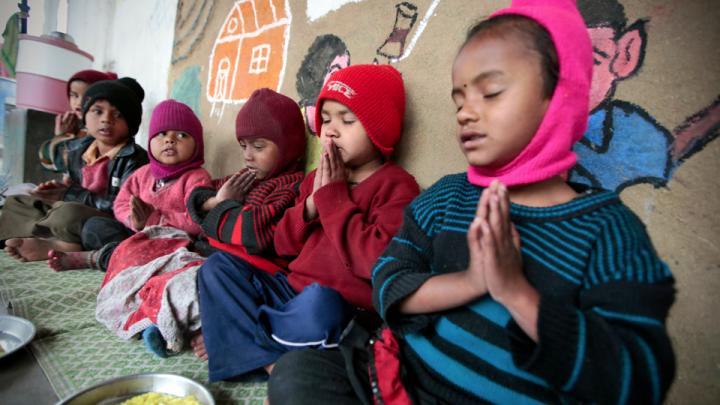
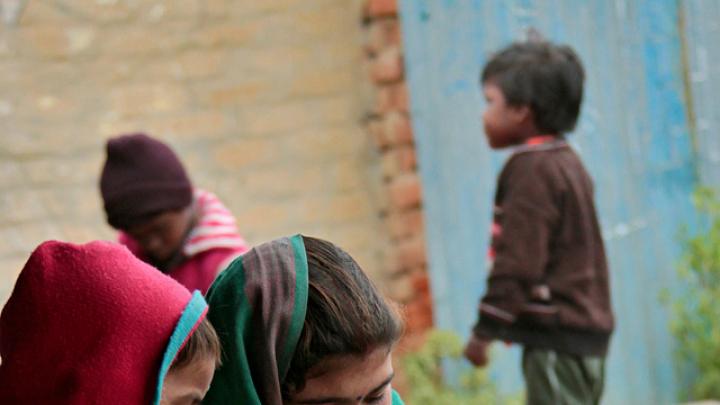
Through research, scholarly articles, and relationship building, Harvard School of Public Health professor Theresa Betancourt—profiled in our November-December issue—seeks to demonstrate models for governments, NGOs, funding organizations, and communities to work together in coordinated ways that ultimately improve children’s lives. Above, see images of the types of disadvantaged children she works with in India—from runaways or those in homeless families who spend their lives around the Jaipur train station to the sons and daughters of the migrant workers who build India’s high-rise offices and dwellings.
Theresa Betancourt: Images from India














You might also like
Talking About Tipping Points
Developing response capability for a climate emergency
Academia’s Absence from Homelessness
“The lack of dedicated research funding in this area is a major, major problem.”
The Enterprise Research Campus, Part Two
Tishman Speyer signals readiness to pursue approval for second phase of commercial development.
Most popular
More to explore
What is the Best Breakfast and Lunch in Harvard Square?
The cafés and restaurants of Harvard Square sure to impress for breakfast and lunch.
How Homelessness is a Public Health Crisis
Homelessness has surged in the United States, with devastating effects on the public health system.
Portfolio Diet May Reduce Long-Term Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke, Harvard Researchers Find
A little-known diet improves cardiovascular health through several distinct mechanisms.