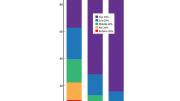
In surveys of wealth-inequality perceptions and preferences conducted by Harvard Business School (HBS) associate professor Michael Norton, respondents always estimate that wealth is more equally distributed in the United States than is actually the case, and say they would like it to be spread around still more evenly.
Harvard respondents are no different; they, too, underestimated how large a portion of the nation’s resources the top quintile controls, and said that in an ideal world, they would allocate an even smaller share to this group. (In their estimation of how wealth is currently distributed, however, Harvardians came closer to the actual distribution than did other populations whom Norton has surveyed, estimating that the top 20 percent controlled 72 percent of the resources. Other groups guessed that the top quintile held less than 60 percent of the wealth; the actual number is more than 80 percent.)
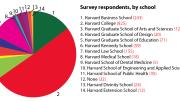
The bulk of the 1,645 valid responses in the Harvard survey, which was promoted on Harvard Magazine’s website from September 23 to October 15, came from men: 70 percent, versus 30 percent from women.
Women in the sample favored significantly more equality than men, wanting to allocate 11 percent of the wealth to the bottom quintile, versus 8 percent for the men.
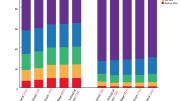
As with other populations Norton has surveyed, both liberal and conservative Harvard alumni estimated that wealth is more equally distributed in the United States than it actually is, and said they wished it were even more equally distributed than they estimated it to be.
Harvard Medical School graduates guessed the most accurately, estimating that the top quintile held nearly 74 percent of wealth. And HBS alumni actually made the most utopian guess, estimating that the top quintile held less than 70 percent of wealth.
Graduates of all five schools said they wanted the distribution to be more equal than they estimated it to be (which, again, was more equal than actual wealth distribution). In this case, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences alumni wanted to give the largest share of resources—10 percent—to the bottom quintile. On the other end of the spectrum, HBS students wanted to give the bottom quintile just under 7 percent of the total wealth.