During two and a half pandemic semesters, instruction throughout the University first pivoted online, and then, after the summer of 2020, evolved into more sophisticated, engaging forms of Zoom-based teaching and some hybrid classes at the Business School (see “School Goes Remote,” November-December 2020, page 29). Peering ahead, what is the future for pedagogy at Harvard?
First things first: even as vaccination proceeds, it is not certain that the campus will be a coronavirus-free environment by late August—nor that every enrolled student will be able to attend classes as in the past. At a minimum, some social distancing may be required, straining the capacity of specialized facilities like teaching labs. International students may be unable to complete vaccinations, or obtain timely visas, in order to enroll at the beginning of the semester—so even as in-person intruction resumes on campus, hybrid offerings (in-class and online) may be required for some time. And as students who deferred admission or opted for time off during the 2020-2021 academic year arrive on campus, they may overwhelm size-limited courses or even the largest teaching spaces, again necessitating some hybrid instruction.
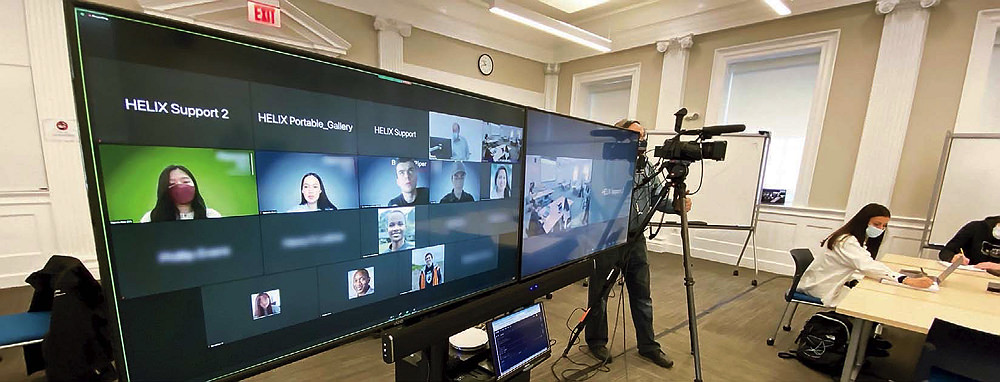
Hybrid teaching with a large projection system enables the instructor to follow remote and in-person learners.
To prepare for these pragmatic possibilities, the Faculty of Arts and Sciences ran pilots involving 14 classes (professors and students volunteered to participate) in April, testing laboratories, language and performing-arts instruction, and larger-format lecture-based classes with hybrid technology. Initial responses were largely positive (see harvardmag.com/fall-teaching-21): as one instructor put it, “I’m really lucky to be part of an institution that makes this kind of investment in its pedagogy—it’s incredible at an R-1 [research-focused] university.” There was unanimity about one aspect of live teaching and learning together: “the great joy and emotion from the students and faculty coming back into the classroom,” as Rebecca Nesson, associate dean of the Harvard College curriculum, who oversaw the pilots, put it. This fall, “It’s going to be very emotional when people come back.”
Pandemic exigencies aside, does it make sense simply to return to the status quo ante? In effect, Harvard has been through an enormous, forced experiment in teaching, applying new technologies to the classroom, and wholesale rethinking by faculty members about how to effect learning. Having authorized the Graduate School of Education to offer its master’s degree online—a precedent—will the Corporation continue down that road? Will professors welcome more “visitors” to enliven their classes, now that it is virtually costless to do so online, versus the time and expense required for someone to fly to Boston? Does it make sense to continue disseminating laboratory supplies and equipment to students at home, so their experiments can draw on local experiences and opportunities? Having learned to scale up online instruction, does Harvard want to extend its reach more widely beyond campus—perhaps much more widely? What will the schools’ role, and the University’s, be in sorting out policies, technological platforms and support, and related issues?
Rather than letting lessons from the pandemic recede as the crisis abates, a task force of deans, faculty members, and others assembled by Bharat Anand, vice provost for advances in learning, is addressing questions like these, trying to get at the future of teaching and learning. The experience gained during the past decade through discussions among interested faculty members organized by the Harvard Initiative for Learning and Teaching, edX and Harvard X courses, and schools’ online operations (see “Rebooting Online Education,” May-June 2020, page 18) have suddenly become familiar to everyone, and at scale. Look for the task force’s findings and recommendations—based on surveys, case studies, and benchmarking against other institutions—in early to mid summer.









