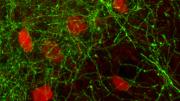
Harvard Medical School (HMS) researchers have identified a specific class of neurons that help synchronize activity in the cortex, triggering brain waves characteristic of consciousness, perception, and attention. The findings, which appear in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences this week, may help to identify therapies in disorders such as schizophrenia.
“This is a move toward a unified theory of consciousness control,” co-senior author Robert McCarley, professor of psychiatry, said in a news release. “We’ve known that the basal forebrain is important in turning consciousness on and off in sleep and wake, but now we’ve found that these specific cells”—basal forebrain GABA parvalbumin neurons (PV neurons)—“also play a key role in triggering the synchronized rhythms that characterize conscious thought, perception and problem solving.”
“Our brains need a coherence of firing to organize perception and analysis of data from the world around us,” McCarley said. “What we found is that the PV neurons in the basal forebrain fine tune cognition by putting into motion the oscillations required for higher thinking.”
According to researchers, different states of mind are defined by distinct waveforms and frequencies in the electrical field of the brain. When the brain is alert and performing complex calculations, the cerebral cortex (where higher-level thinking takes place) thrums with cortical band oscillations in the gamma wavelength; in some neurological disorders like schizophrenia, these waves are out of tune. Understanding the mechanism the brain uses to sync up for conscious thought may suggest potential therapies for disorders like schizophrenia where the brain fails to form these characteristic waves, McCarley said.