In 1933, Joseph Stalin engineered a genocide that led to the death by starvation of an estimated four million Ukrainians. Stalin set unreachable grain production quotas on farmers, and then, when the quotas were not met, confiscated all the grain to feed an urbanizing, industrializing U.S.S.R. In so doing, he orchestrated what is well known in Ukraine as the “Holodomor,” or “death by hunger.” Now, nearly a century later, Vladimir Putin has deployed a variant of Stalin’s food-based strategy as part of his own war tactics in Ukraine, bombing and blocking main ports to nearly halt exportation of grain. All this reminds Ukrainians, and the world, of how Ukraine has suffered at Russia’s hands in the past; and how the current situation has dire implications for many poorer countries which are being cut off from desperately needed Ukrainian grain.
Larysa Kurylas, M.Arch. ’85, a Washington, D.C., architect who is the daughter of Ukrainian immigrants, is not surprised by this echo of the horrific events of 1933. She designed the sculpture, Field of Wheat, a Holodomor memorial in Washington, that was commissioned by the Ukrainian government through an international competition in 2009. Since its dedication in 2015, Field of Wheat has become a regular stop for Ukrainian dignitaries visiting the United States: Volodymyr Zelensky paid his respects there in September 2021, months before Russia’s invasion began in February. In light of events since, Kurylas’s sculpture is no longer just a memorial to the past.
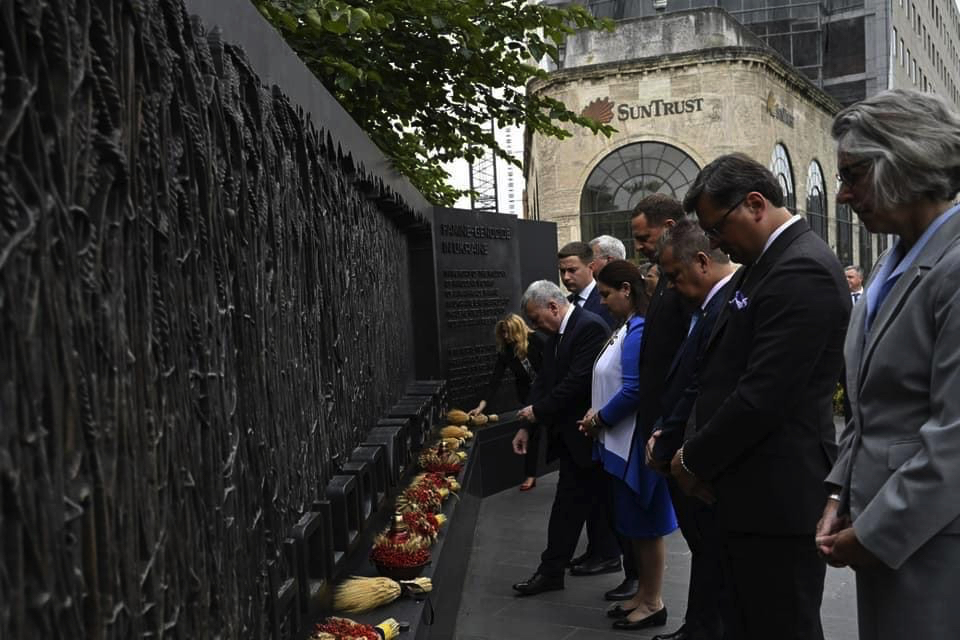

Larysa Kurylas (far right) pictured with dignitaries paying their respects, including Dmytro Kuleba, Foreign Minister of Ukraine, in September 2021.
Photograph courtesy of Larysa Kurylas
On July 22, Ukraine and Russia signed an agreement, brokered by the United Nations and Turkey, to re-open Ukrainian Black Sea ports and resume grain exports. Less than 24 hours later, Russia’s military bombed Odesa, Ukraine’s largest port for grain exports, dimming the prospects for successful implementation of the deal.
Kurylas says she felt “duty-bound” to participate in the Ukrainian government’s competition for the design of a Holodomor Memorial. Most Westerners, she knew, were unaware of the cultural and political significance of wheat grain in Ukrainian history. Indeed, the blue and yellow Ukrainian national flag reflects blue skies over golden wheat fields. And the Holodomor famine wasn’t officially recognized as a genocide until 2006, long after the fall of the Soviet Union.
Nevertheless, says Kurylas, “Most Americans know Ukraine as the breadbasket of Europe.” That’s one reason she chose to use wheat in the memorial design. And obviously, she notes, “Wheat was, and continues to be, weaponized.”
The memorial, located just outside of Columbus Circle in Washington, D.C., is a 30-foot-long bronze, bas-relief sculpture, which means the casting forms a wall. On its surface, highly detailed wheat heads appear in clear relief on the left but gradually fade and disappear to the right. As Kurylas explains in a studio description of her work, this effect is intended to “symbolize the emptiness of lives lost in the Holodomor but, as an extremely willful sculptural act, it reflects the artificiality of the famine.”
At the time of its design, she wrote, “The Memorial is to serve as a living reminder—in the capital of the free world—of the need to prevent such politically motivated tragedies from happening in the future.”
Installed originally to commemorate the lives lost, Field of Wheat now reminds Americans that Putin’s strategy is not entirely an original one. The grain, a source of life to the Ukrainian people, has for more than a century also been the source of death, war, and destruction. The memorial now encompasses all of this history.
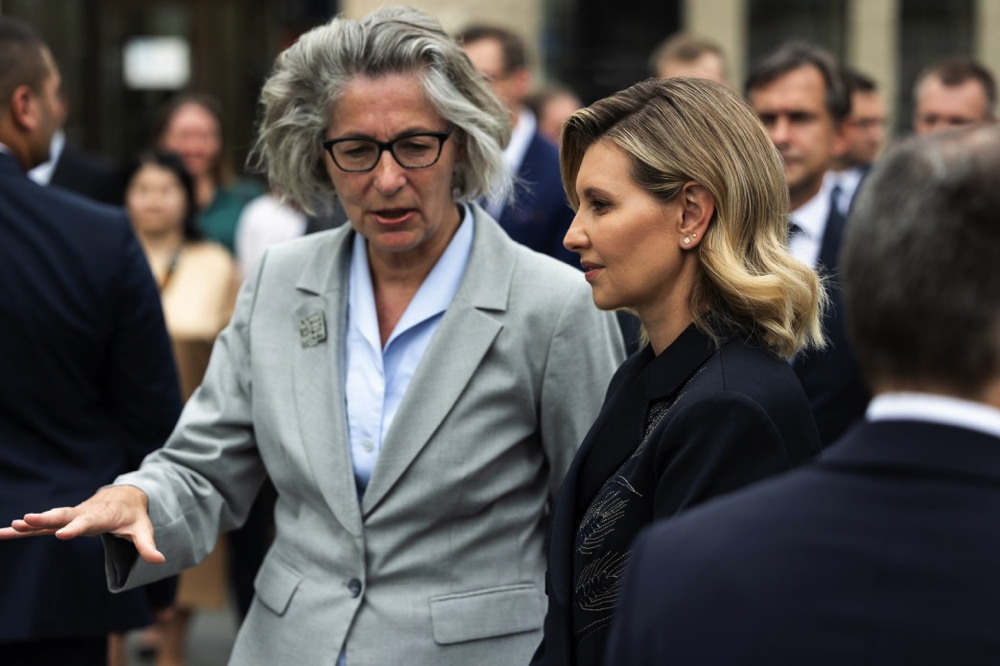

Larysa Kurylas and Ukranian First Lady Olena Zelenska
Photograph courtesy of Larysa Kurylas
On July 18, Ukrainian First Lady Olena Zelenska visited “Field of Wheat” before pleading to Congress for more air defense weaponry. Her words perhaps capture the sculpture’s dynamic role in time: “Through all this suffering and pain, we send a strong warning to the war: Remember the darkest past can be easily beaten,” she said. “In certain places, the darkness has never faded away.”