Cell phones automatically keep track of the nearest cell tower, which is why phone records can be used to determine where people were at a particular time—a principle already employed to generate alibis and convictions in the legal world. Now, researchers at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (HSPH) have found a potentially life-saving use for these cell-phone records: to predict the spread of epidemic diseases.
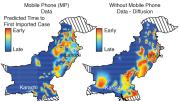
By combining the phone records of around 40 million Pakistani mobile-phone subscribers (representing 22 percent of the country’s population) with climate data, the Harvard group was able to predict the spreading patterns of dengue fever, a potentially deadly tropical disease endemic in that nation. The investigators matched the trajectory of the dengue virus in a 2013 epidemic to the traveling pattern of mobile users, and found that the latter could predict the former fairly accurately. “This provides a more accurate forecast of where dengue is going to [appear] as compared to other approaches that use environmental variables or proxies of human movements like road networks,” says Caroline Buckee, senior author of the study and an assistant professor of epidemiology. For low-income countries without well-developed road networks, mobile data can be particularly helpful for tracking the spread of epidemics, adds Amy Wesolowski, a postdoctoral research fellow and lead author of the study.
Forecasting outbreaks is crucial for controlling the spread of dengue fever, which has no vaccine or treatment. Preparedness—tracking when and where it will happen—is “one of the only things you can do,” says Buckee. Because the disease spreads mainly in urban areas, where cell-phone penetration tends to be higher, dengue lends itself particularly well to tracking by proxy using mobile networks. According to Wesolowski, the authors are working to present the findings to Pakistan’s health officials.
The Harvard study represents the largest data set of mobile-phone records ever analyzed to estimate human mobility. It was enabled by a collaboration with Telenor, the second-largest provider of mobile telecommunication services in Pakistan, and the researchers went to great lengths to protect the privacy of the company’s subscribers. The cell-phone records were anonymized, Buckee says, in the hope that the study will set a good precedent for future collaborations between health researchers and the telecommunications industry.