In April, a SpaceX rocket carried a commercial communications satellite to a geostationary orbit more than 22,000 miles above the equator. The satellite carried an important payload: a $93-million instrument for measuring pollution across North America, developed at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA). The Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO) device uses spectroscopic analysis of trace atmospheric gases to pinpoint sources and track plumes of air pollution anywhere on the continent, from the Canadian tar sands in the north to points as far south as Mexico City and Cuba.
In the event of wildfires or industrial accidents, TEMPO can observe in intervals as brief as 10 minutes. In the future, via an app, the data it gathers will provide hourly chemical weather forecasts to anyone who wants to know, for instance, when they should or shouldn’t go for a run. And it is expected to lead to new insights into daily cycles of pollution, the formation of atmospheric rivers (which can carry huge quantities of moisture), the processes by which agricultural activities intensify heat waves in the Midwest, and how naturally occurring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) interact with man-made pollutants to harm human health.
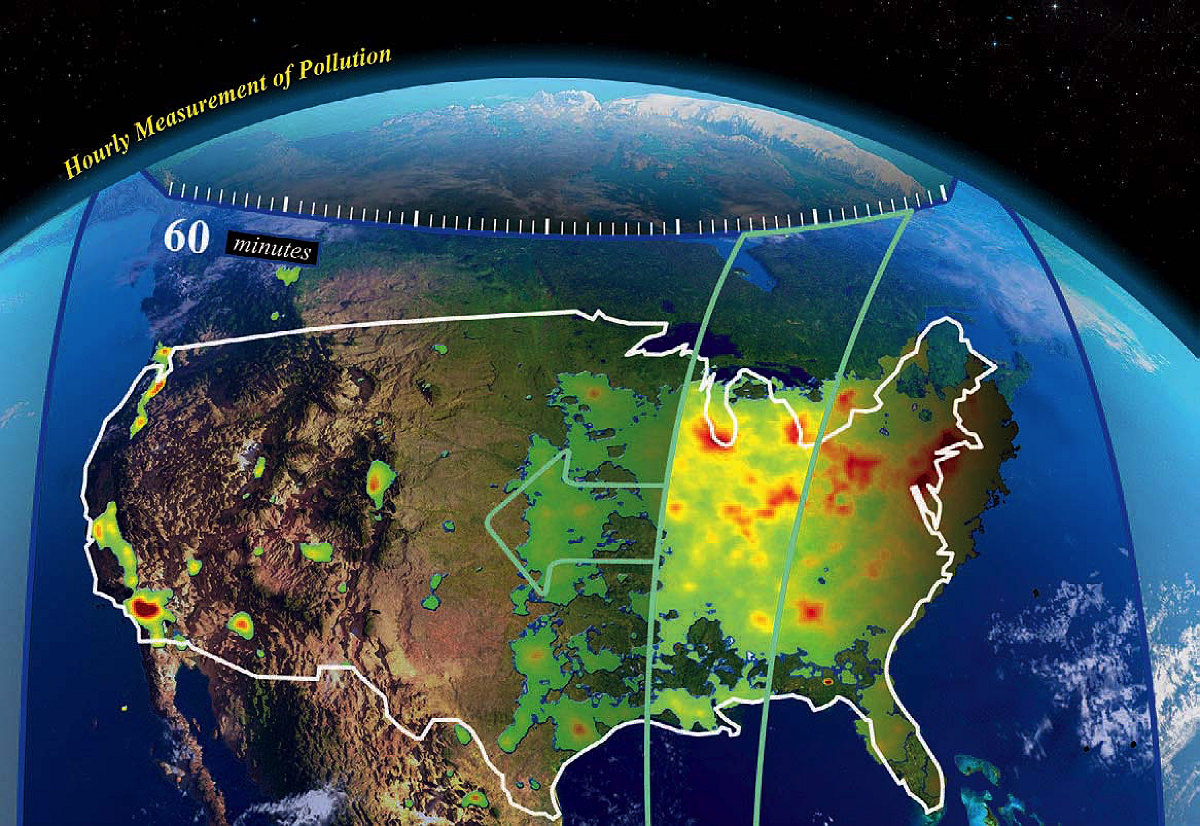
A geostationary satellite will measure air quality by scanning the country every hour for pollutants.Graphic (left) courtesy of Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics/NASA
The National Academy of Sciences first identified the need for geostationary observation of air quality over the continental United States more than a decade ago. Existing satellites for detecting pollution typically orbit the Earth multiple times a day, passing over the same point just once daily at a fixed time, taking a single measurement at that location. A satellite that passes over Manhattan at 1:30 P.M., for instance, will miss the air pollution associated with morning and evening commutes. And ground-based monitors tend to be concentrated in cities and can’t track air pollution as it is carried in different directions by the wind. A sister satellite owned by South Korea now makes similar measurements above Asia, and another sponsored by the European Space Agency is expected to launch in 2024, thus creating a network of satellites that can track air pollution over land in most of the Northern Hemisphere.
McCoy Family professor of atmospheric chemistry and environmental engineering Daniel Jacob was asked at the time to lead a NASA committee charged with determining the important scientific objectives and, he says, “how that would track to the design of an instrument.” Jacob is especially interested in the international transport of air pollution. The United States has been “working vigorously for 50 years” to clean its air, he points out, but still, “we’re in violation of air quality standards. We’re getting to the point where a lot of our pollution, I think, is coming from abroad. The way we can see this is from geostationary orbit.”
But TEMPO’s capabilities are extensive, and other researchers are interested in using the terabyte of data it yields each day to track how air pollution is transported across state borders; help farmers decide how much fertilizer to apply to crops (it can detect nitrogen emitted from soil); or establish why, for example, urban air pollution is worse in lower-income communities. As much as 25 percent of the instrument’s observation time may be used to conduct novel experiments.
Kelly Chance, Ph.D. ’78, leads the TEMPO project. Jacob describes him as the “ultimate expert on satellite observations” of the atmosphere—although it took a team of hundreds, including NASA project managers and engineers at Ball Aerospace (beyond the core CfA team, including Chance, Xiong Liu, Raid Suleiman, John Davis, John Houck, Caroline Nowlan, Huiqun Wang, and Gonzalo González Abad), to design and build the instrument. The device measures visible light and ultraviolet radiation from the sun as it is scattered back into space after passing through Earth’s atmosphere. By analyzing absorption of the light at specific wavelengths, it can determine what gases are present in a column of air between the satellite and a rectangular area on the ground that is about the size of the Los Angeles airport. But with averaging, it can effectively measure pollution in smaller grids, about one square mile in size, explains Erika Wright, the education specialist on the CfA’s TEMPO team: the satellite jitters a little bit as it scans from east to west, taking overlapping observations hourly that enable researchers to “narrow down where that poor air quality really is concentrated.”
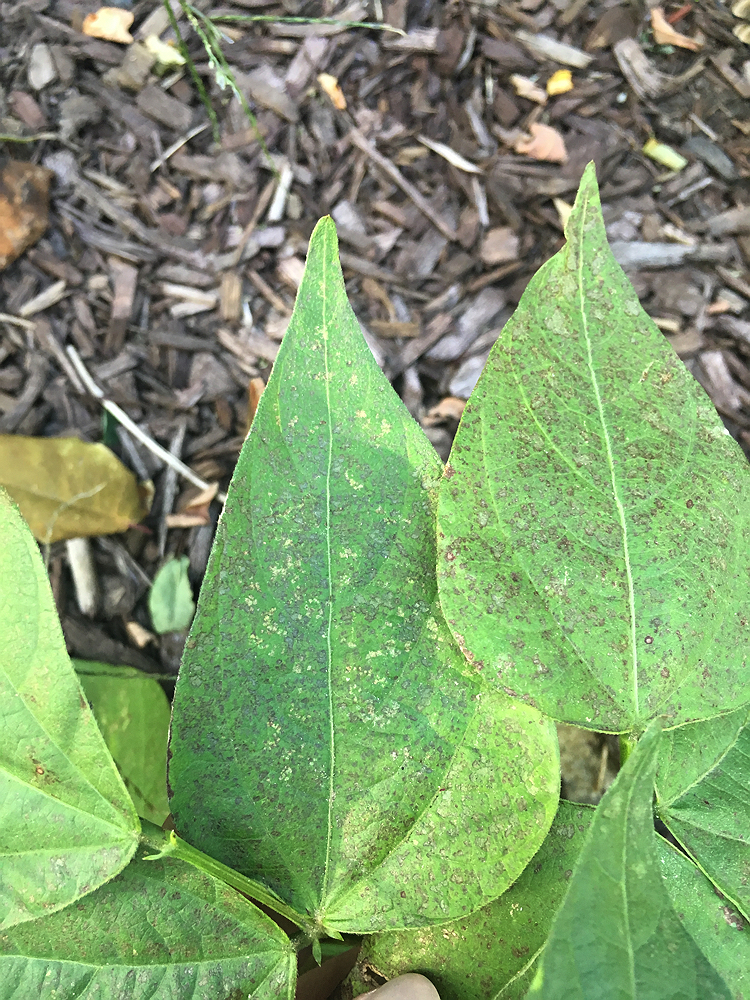

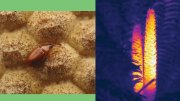
Ground level ozone is harmful to people and crops, such as these ozone-damaged snap bean leaves.
Photograph courtesy of Center for Astrophysics
Once calibrated against terrestrial instruments and low-Earth orbit satellites, TEMPO will measure several gases regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency: nitrogen dioxide, a poisonous gas that is part of tailpipe and power plant emissions; sulfur dioxide, mostly from power plants; formaldehyde, which is a proxy for VOCs from both man-made and natural sources—such as those emitted principally by the chemical and petrochemical industries or those produced by forests under heat stress; and ozone, which forms when nitrous oxides react with VOCs in the presence of sunlight and heat. Critically, TEMPO will be able to distinguish between ozone high in the atmosphere, where it protects life from damaging radiation, and near the ground, where it harms humans, animals, and plants—including crops. In fact, as part of the education outreach associated with TEMPO, Wright has established a network of ozone bioindicator gardens across the country, where people will be able to see the injury ozone does to leaves. Given that air pollution is responsible for more than 70,000 premature deaths in the United States annually and is linked to a variety of illnesses, the gardens are a tangible reminder of the impacts of this invisible gas.