A study led by professor of economics Raj Chetty found that students who had the best kindergarten teachers had higher incomes in adulthood. Below, slides that explain some of his results.
Courtesy of Raj Chetty
Courtesy of Raj Chetty
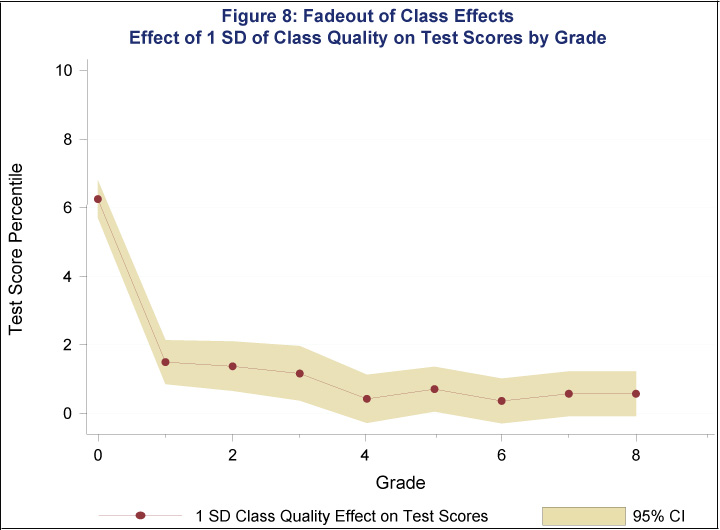
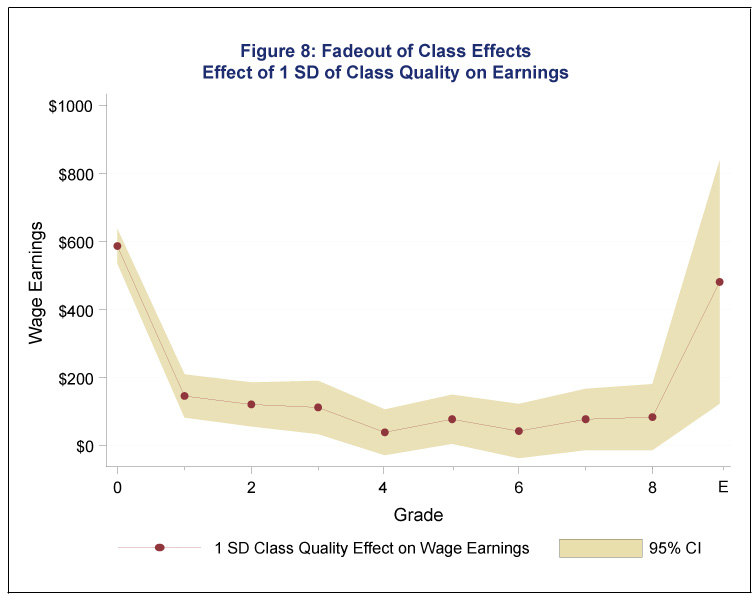
The first panel of Figure 8 (top) shows that the effects of a good kindergarten classroom environment on test scores drop off, and virtually disappear, in the later grades. The second panel (above) shows the predicted impact on earnings in adulthood based on test score gains made in each grade. Because test score gains are small in later grades, one would not predict much of an earnings gain based on students' performance in these later grades. But the chart shows that the impact of a good kindergarten class reemerges in adulthood.

Courtesy of Raj Chetty
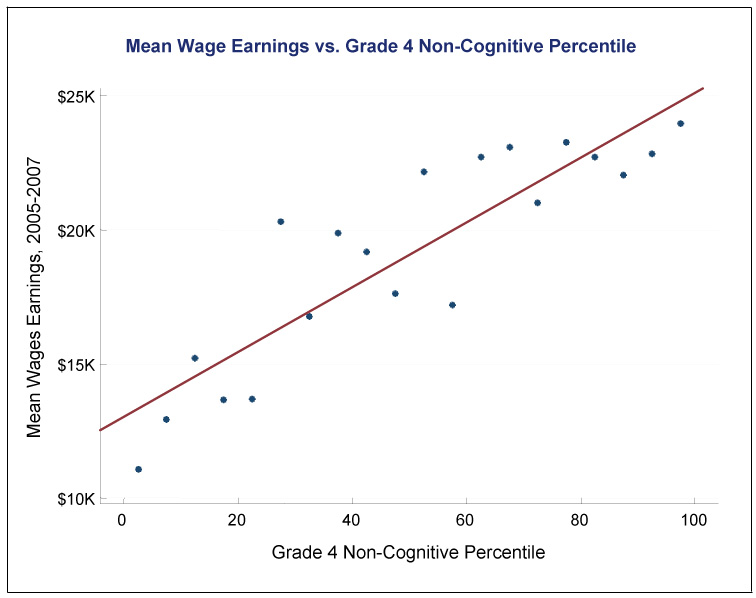
Most analysis of the Project STAR data (a study of nearly 12,000 Tennessee kindergartners in the mid 1980s) focused on math and reading test scores, but Chetty's team also examined non-cognitive measures.
Courtesy of Raj Chetty
They found a nearly linear relationship between students' non-cognitive scores (measured in grade 4) and their wages in adulthood.
Courtesy of Raj Chetty
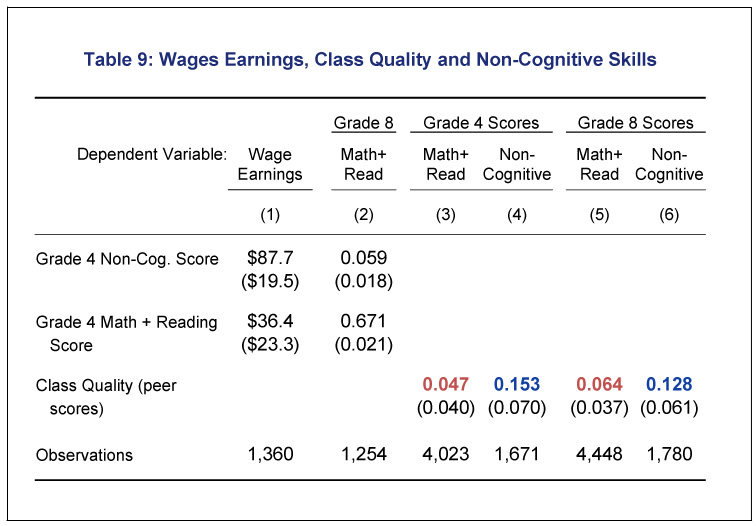
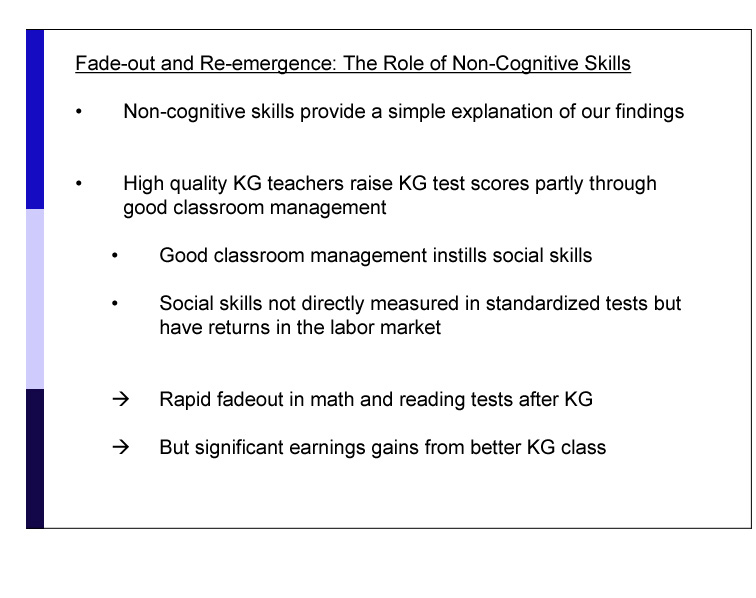
Unlike the impact on math and reading test scores, which disappears in later grades, the impact of being in a better kindergarten class on non-cognitive measures (such as those described in the slide above) persist even in fourth and eighth grade. Improvements in non-cognitive outcomes could therefore explain why a good kindergarten class has long-lasting impact that persists even into adulthood.
Courtesy of Raj Chetty
Courtesy of Raj Chetty
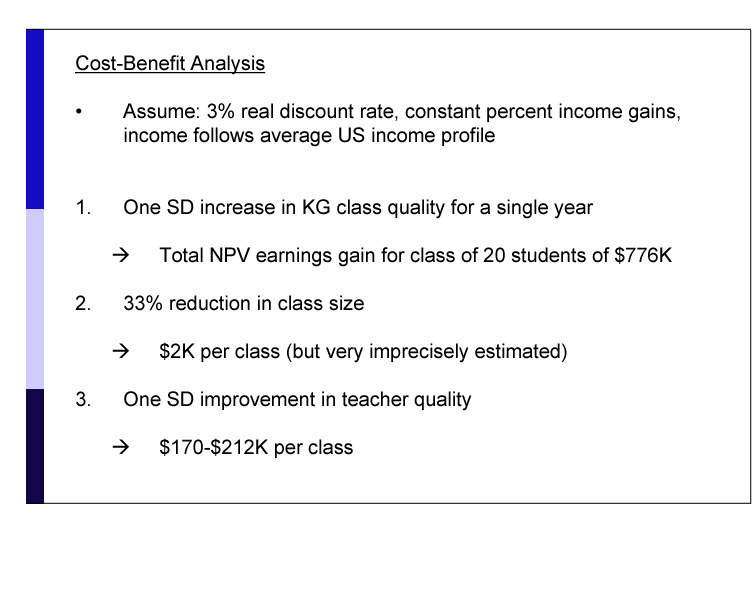
Chetty's team found that in a classroom whose quality was one standard deviation higher than the mean, the resultant increase in earnings over the course of a lifetime, for all students in the class combined, was $776,000. Reduction in class size had a smaller positive effect.








