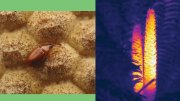
Growing up in Lutheran Sweden, Karin Öberg had no inkling that she would one day become an astrochemist, the first to observe a complex organic molecule in the freezing cloud of gas and dust surrounding a young star—or that she would convert to Catholicism. As a young student, she was interested in literature, history, and art; and it was philosophical questions about “who we are, where we come from” and the origins of the universe that made her think, as she neared college and decided to pursue science, that physics and astronomy were the most interesting fields to study. But in the competitive environment at Caltech, she learned her aptitude was for chemistry: “I had to choose. Do I go with my heart, or my talent?” She chose chemistry, before discovering she could apply that talent to important questions in astrophysics. One such big question is, Are the chemical antecedents of life present outside the solar system? To explore this, Öberg, professor of astronomy, studies ice chemistry in her lab. “The clouds where stars and planetary systems form are close to absolute zero,” she says. “If a molecule hits a grain of dust, it will stick and form an ice made of water, dry ice, or [carbon monoxide]. Any chemistry is going to happen either on top of this icy layer or inside the ice.” The James Webb Space Telescope now enables her to study the composition of these icy grains among the inner regions of distant solar systems, where Earth-like planets form in the “habitable zone.” Could the precursors of life exist there? Some questions only science can answer, with others better suited to theology. Whether intelligent life exists elsewhere, she says, is a question on which both her science and religion are currently “agnostic.”
Karin Öberg
Karin Öberg
This astrochemist studies the chemical antecedents of life in the universe.

Karin ÖbergPhotograph by Stu Rosner
You might also like
Are ‘Little Red Dots’ Keys to Understanding the Early Universe?
Harvard-Smithsonian astrophysicist Fabio Pacucci explains one of cosmology’s newest mysteries.
What Do Puppies Know?
Canine capabilities emerge early and continue into adulthood.
Research in Brief
Cutting-edge discoveries, distilled
Most popular
Explore More From Current Issue

How Stories Help Us Cope with Climate Change
The growing genre of climate fiction offers a way to process reality—and our anxieties.

How a Harvard and Lesley Group Broke Choir Singing Wide Open
Cambridge Common Voices draws on principles of universal design.