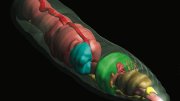
Even to a trained zoologist, one earthworm looks very much like the next. So much so, in fact, that one species generally can’t be distinguished from another just by looking—unless the animal has been painstakingly dissected. Exposing its internal morphology in this way destroys the specimen. The earthworm at right, with its life systems laid out in color, was “wild caught,” according to its record in Harvard’s Museum of Comparative Zoology (MCZ) specimen database, MCZbase. Aporrectodea caliginosa, a common species, was collected in the vicinity of 26 Oxford Street in Cambridge, where the museum is located. “You can imagine the drama” of its capture, quips James Hanken, Agassiz professor of zoology, curator in herpetology, and director of the MCZ.
What makes this lowly worm special is that it has been scanned using micro-computed tomography (microCT). The technology allows investigators to peer inside, to “see” the worm’s internal structures, including the digestive tract (pink), nervous system (yellow), and circulatory system (blue). Each can be studied separately and rotated in space in any direction to facilitate close inspection.
Before the MCZ tried it, no one had used a microCT scanner to image museum specimens, and the project has become an enormous success. The ability to see the reproductive organs, for example—the seminal vesicles, the number of testes and ovaries, and the spermathecae—has allowed researchers to dispel the “taxonomic chaos” that has plagued the study of earthworms.
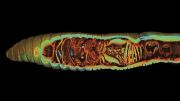
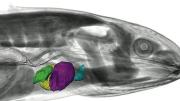
But the applications are far broader. Such imaging allows the noninvasive study of extinct or critically endangered creatures in the MCZ’s 20-million-plus specimen collections, such as the larval axolotl at left above. Assistant professor in organismic and evolutionary biology Stephanie Pierce, curator of vertebrate paleontology at the MCZ, explains that one of her students has imaged the skulls of anole lizards (at left below) to look at how the inner-ear system (specifically, the delicate vestibular system so crucial for balance and spatial orientation, not depicted here) relates to the braincase bones, and how the vestibular system changes with habitat segregation on islands. For the MCZ, home to the largest university-based natural history collection in the world, treasured specimens can now be safely examined and shared with researchers and students, illustrators, artists, conservationists, and teachers worldwide.